Urban Heat Island Mitigation and Civil Engineers
Urban Heat Island Mitigation and Civil Engineers
Introduction
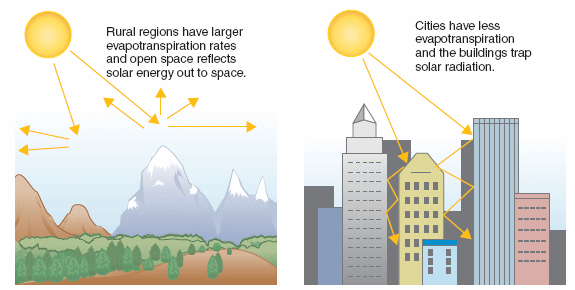
Urban Heat Island (UHI) is a phenomenon that occurs in cities and urban areas, where the temperature is significantly higher than in the surrounding rural areas. The main reasons for the UHI effect are the lack of vegetation, buildings, and other infrastructure that absorb heat during the day and release it during the night. The temperature difference between urban and rural areas can be as high as 10 degrees Celsius. UHI has significant environmental and health impacts, including increased energy consumption, air pollution, heat-related illnesses, and even mortality. This essay will explore the role of civil engineers in mitigating the UHI effect.
The UHI Effect
The UHI effect occurs when the heat generated by human activities, such as transportation, industrial processes, and buildings, is trapped in the urban environment. Urban areas typically have fewer trees and green spaces than rural areas, which means less shade and less cooling through evapotranspiration. Additionally, buildings and roads absorb and re-emit heat, further contributing to the UHI effect. The UHI effect can lead to increased energy consumption for cooling and heating buildings, increased air pollution, and heat-related illnesses.
Mitigating the UHI Effect
Mitigating the UHI effect requires a multi-disciplinary approach that involves urban planners, architects, landscape architects, and civil engineers. Civil engineers play a critical role in mitigating the UHI effect by designing and implementing green infrastructure, such as green roofs, green walls, and urban forests, and developing sustainable construction practices that reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Green Infrastructure
Green infrastructure refers to natural and semi-natural systems that provide ecological and social benefits. Green infrastructure can include green roofs, green walls, urban forests, and permeable pavements. Green roofs and green walls provide insulation and cooling for buildings and can reduce energy consumption for cooling and heating. Urban forests and green spaces can reduce the ambient temperature by shading and cooling the air through evapotranspiration. Permeable pavements allow rainwater to infiltrate into the ground, reducing runoff and cooling the pavement.
Sustainable Construction Practices
Sustainable construction practices can also play a critical role in mitigating the UHI effect. Sustainable construction practices can include using sustainable materials, such as recycled materials and low carbon concrete, designing buildings that maximize natural ventilation and daylighting, and implementing energy-efficient technologies, such as solar panels and geothermal systems. These practices can reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with building construction and operation, contributing to mitigating the UHI effect.
Case Studies
Several case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of green infrastructure and sustainable construction practices in mitigating the UHI effect. For example, the installation of green roofs in Chicago has been shown to reduce the ambient temperature by up to 3 degrees Celsius. In New York City, the MillionTreesNYC program aims to plant one million trees by 2030, which is expected to reduce the ambient temperature by up to 1.5 degrees Celsius. In Singapore, the government has implemented a green roof program, which has resulted in a 10% reduction in energy consumption for cooling and heating buildings.
Conclusion
The UHI effect is a significant environmental and health challenge in urban areas, and civil engineers have a critical role to play in mitigating this effect. Civil engineers can design and implement green infrastructure and sustainable construction practices that reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions and provide cooling and shading for buildings and public spaces. Green infrastructure and sustainable construction practices can have multiple benefits, including reducing energy consumption, improving air quality, and enhancing the quality of life for urban residents. Civil engineers must continue to develop innovative solutions to mitigate the UHI effect and create more resilient and sustainable urban environments.
Comments
Post a Comment